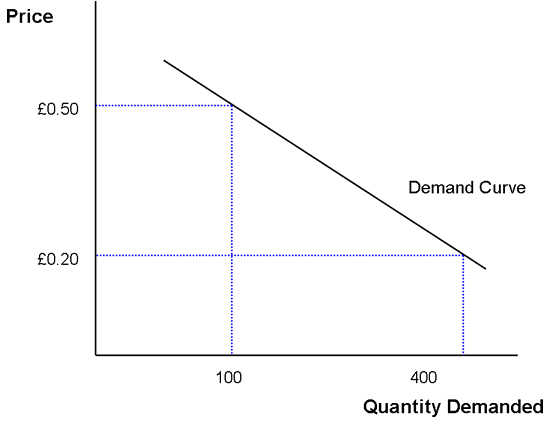
Elasticity of demand-Measure of how consumers react to a change in price -(taking a stab at things)
Elastic demand-demand that is very sensitive to a change in price E>1 the product is not a necessity, and their are available substitutes (cookies)
InElastic demand-Is not very sensitive to a change in price E<1 the product is a necessity, their are few to no substitutes, people will buy no matter what (water)
Unit/Unitary elastic-E=1
Formula's
TFC + TVC = TC
AFC + AVC = ATC
TFC/Q = AFC
TVC/Q = AVC
TC/Q = ATC
TFC = AFC x Q
TVC = AVC x Q
MC = new TC - old TC
Price of Elasticity of Demand (PED)
Step 1: Quantity
New Quantity-Old Quantity/old quantity
Step 2: Price
New Price- Old Price/ old price
Step 3: PED
% Δ in quantity demanded/ %Δ in price = PED
Total Revenue-Total amount of money a firm receives from selling goods and services
TR=PxQ
Fixed Cost-a cost that does not change no matter, how much is produced
Ex:Rent, Mortgage,Insurance,Salaries
Variable Cost-a cost that rises or falls depending upon how much is produced
Marginal Cost- the cost of producing one more unit of a good
MAY THE FORCE BE WITH YOU